Feb 28, 2025
Articles
4 Best Practices for Food Manufacturing Compliance

Martín Ramírez

Food manufacturing compliance is about following the rules while also protecting public health, maintaining trust, and keeping operations running smoothly.
Regulatory requirements are strict for a reason, but instead of seeing them as hurdles, manufacturers should treat compliance as an opportunity to strengthen processes, improve efficiency, and ensure product quality.
The key is to understand the rules and make them a natural part of daily operations.
This guide breaks down the essentials, from regulatory frameworks to practical strategies that help you stay ahead of compliance challenges without disrupting production.
The Regulatory Framework for Food Manufacturing
Before diving into best practices, let’s go over the key regulatory agencies that oversee food manufacturing:
FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulates most food products and enforces the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) and Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP). These focus on proactive food safety measures.
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) oversees meat, poultry, and eggs. It enforces Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), which helps identify and control potential hazards.
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) ensures worker safety by enforcing sanitation and equipment safety regulations.
Understanding these requirements is only the first step because:
FSMA shifts food safety from a reactive model to a proactive one.
CGMP sets hygiene and sanitation standards.
HACCP establishes risk-based controls to minimize contamination.
Compliance is not a passive process. It requires a deliberate and systematic approach.

Now, let’s look at how to turn these regulations into effective practices.
4 Best Practices for Food Manufacturing Compliance
While regulations provide the framework, compliance requires a structured, ongoing commitment to food safety.
Here’s how manufacturers can ensure they meet and exceed regulatory requirements.
1. Develop a Strong Food Safety Plan
A food safety plan is not a suggestion. Most food businesses, including processors, retailers, and food service establishments, are legally obligated to have a food safety plan.
So, every facility must develop and maintain a structured plan that addresses potential risks and outlines clear preventive measures.
Core Components of an Effective Food Safety Plan
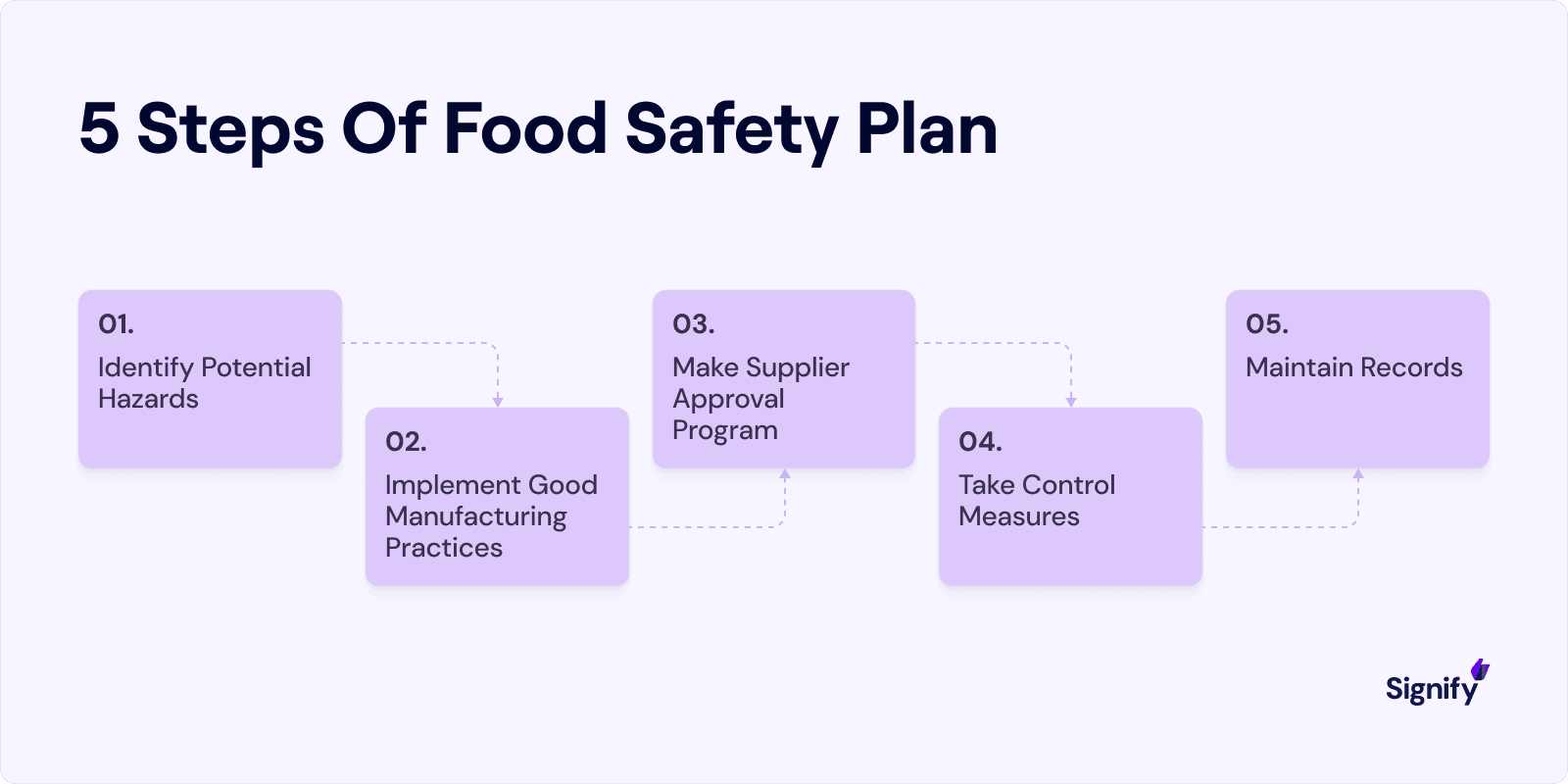
Hazard Identification: Assess biological, chemical, and physical hazards at every stage of production, including raw materials, storage, processing, and packaging.
Preventive Controls: Implement strict measures such as temperature control, cross-contamination prevention, and sanitation protocols.
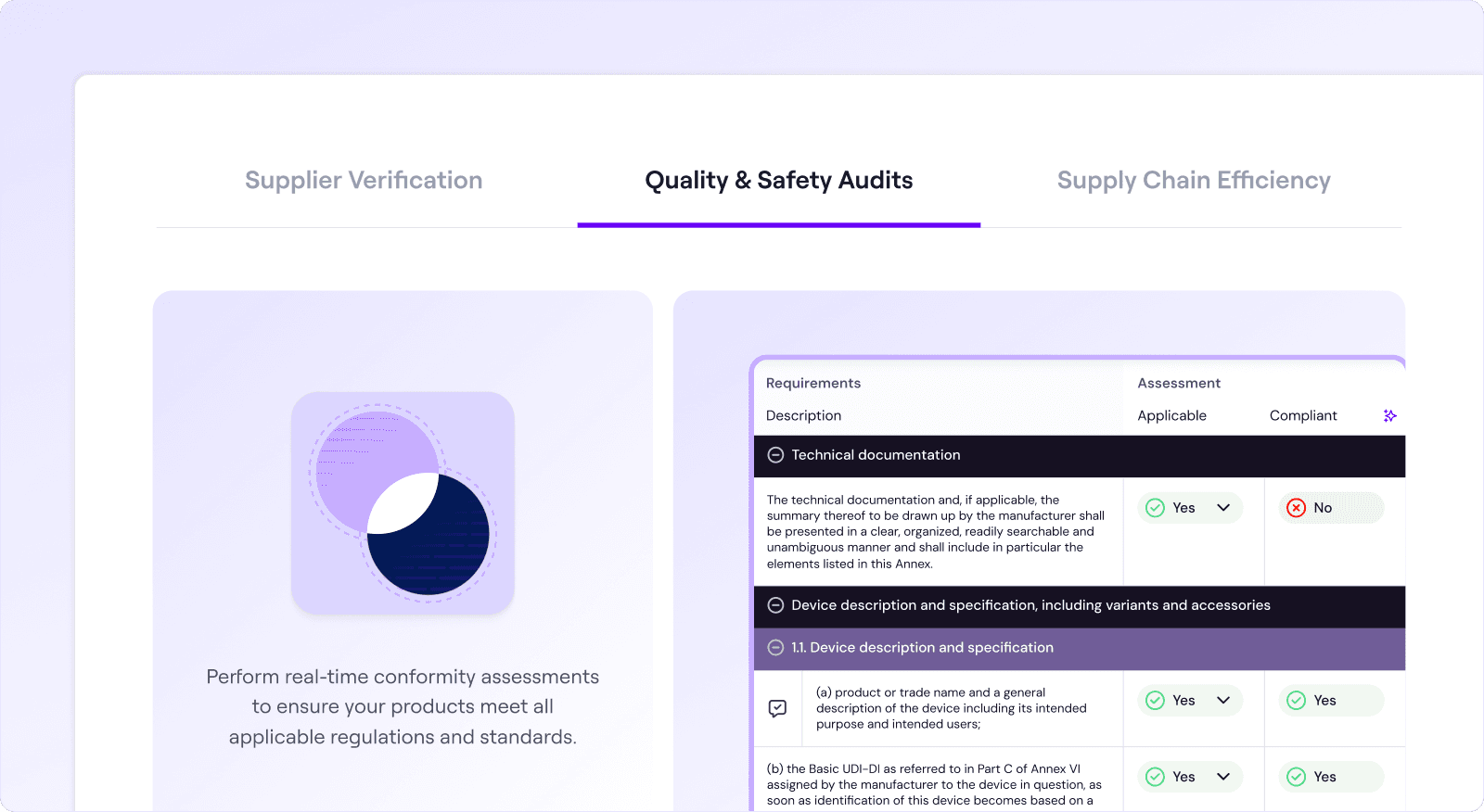
Monitoring Systems: Use automated tracking tools like Signify and real-time data collection to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Corrective Actions: Establish predefined procedures for handling deviations, including product recalls and production shutdowns when necessary.
Employee Training: Require all personnel to undergo regular food safety education and demonstrate competency in hygiene, sanitation, and contamination prevention.
Rather than viewing compliance as a regulatory burden, as a manufacturer, you should integrate these processes into your standard operating procedures (SOPs) to enhance efficiency and food safety simultaneously.
2. Implement a Comprehensive Sanitation Program
Sanitation is more than a routine task. It is a critical control point that directly impacts food safety and regulatory compliance.
Poor sanitation can result in severe consequences, including product recalls, legal action, and reputational damage.
How to Build a Strong Sanitation Program
A Master Sanitation Schedule: Assign cleaning tasks to employees, outlining frequency and scope (e.g., daily equipment cleaning, weekly deep cleans). A structured schedule prevents the buildup of residue that can harbor bacteria.
Hygiene Protocols: Enforce handwashing, protective clothing use, and strict personal hygiene standards for employees. Implement "hygiene zones" within the facility where workers transition from regular areas to sanitized production spaces.
Sanitation Validation: Conduct ATP swab tests to verify cleanliness, ensuring sanitation processes are effective. ATP testing can help identify microbial contamination even when surfaces appear clean.
Allergen Management: Implement measures to prevent cross-contact between allergen-containing and allergen-free production lines. This may involve using dedicated equipment, labeling allergens clearly, and enforcing strict cleaning protocols between production runs.

3. Strengthen Supplier and Ingredient Traceability
Even the most carefully controlled manufacturing environment can be compromised by a weak supply chain.
Without full visibility into ingredient sourcing, manufacturers face significant risks, including contamination, fraud, and regulatory violations.
Key Strategies for Supply Chain Compliance
Supplier Audits: Regularly inspect supplier facilities and require compliance with industry certifications such as GFSI (Global Food Safety Initiative).
Ingredient Testing: Conduct microbiological and chemical testing of raw materials upon receipt.
Blockchain-Based Traceability: Use blockchain technology to create an unalterable record of ingredient origins, movement, and storage conditions.
Cold Chain Monitoring: Ensure temperature-sensitive products remain within safe limits during transport and storage.
Pro Tip:
Leverage Signify's Supplier Verification feature to confirm that all suppliers comply with relevant standards and regulations. This tool streamlines the verification process, enhancing confidence in selecting reliable and ethical suppliers.

4. Conduct Regular Compliance Audits and Emergency Preparedness Drills
Compliance isn’t a one-time effort. It requires continuous monitoring and improvement. So, invest time and effort into regular audits and emergency preparedness drills to stay ahead of potential risks.
Steps for an Effective Audit and Recall Plan
Routine Internal Audits: Conduct monthly inspections to ensure compliance with CGMP and HACCP requirements.
Third-Party Audits: Engage external auditors for unbiased evaluations and industry certification.
Mock Recalls: Test traceability systems by running simulated product recalls.
Staff Training on Crisis Management: Educate employees on proper response procedures for contamination incidents or regulatory inspections.
Pro Tip:
Achieve effortless compliance with AI checklists! Identify gaps, track progress, and maintain industry standards with dynamic, custom-tailored tools that boost efficiency.
This proactive approach eliminates the need for manual gap analysis and ensures that your operations are always aligned with current regulations.
Lessons in Food Safety
Here are examples of successful compliance programs in food manufacturing that demonstrate effective practices and strategies:
1. Mars, Inc.
Mars faced a significant challenge when it had to recall millions of confectionery bars due to contamination with plastic pieces.
The company utilized its efficient supply chain management systems and governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) controls to quickly identify the root cause of the issue.
They traced the contaminant back to a specific factory and tracked affected batches effectively, showcasing the importance of robust traceability systems in compliance management.
2. Blue Bell Creameries
After a listeria outbreak in 2015, Blue Bell Creameries overhauled its compliance program by implementing a comprehensive food safety plan that included stringent monitoring and preventive measures.
The company focused on improving sanitation practices, employee training, and hazard analysis, which helped restore consumer trust and ensure compliance with FDA regulations.
3. Chipotle Mexican Grill
Following multiple food safety incidents, Chipotle implemented a rigorous food safety audit program and enhanced staff training initiatives.
The company adopted a culture of compliance by involving employees at all levels in food safety practices and regularly conducting mock recalls to prepare for potential contamination events.
This way, they have significantly improved their compliance standing and operational efficiency.
4. Peanut Corporation of America
The 2009 Salmonella outbreak linked to Peanut Corporation of America highlighted the consequences of poor sanitation oversight.
In response, many companies in the industry adopted more stringent sanitation protocols and traceability measures to prevent similar incidents.
Compliance as Your Competitive Advantage
If you approach compliance as just another regulatory requirement, you are missing a powerful opportunity.
The most successful food manufacturers do not just aim to meet the bare minimum.
They build compliance into their company culture, making it a driver of efficiency, trust, and long-term growth.
When you take a proactive stance on food safety and compliance, you are not just protecting your business – you are strengthening it as well.
A well-structured compliance program reduces the risks of contamination, product recalls, and legal action. More importantly, it builds consumer confidence.
Shoppers are more informed than ever, and they expect transparency and accountability from the brands they trust.
By integrating food safety and sanitation into your everyday operations, you can:
Reduce costly disruptions by preventing regulatory violations before they happen
Streamline production with well-documented processes that improve efficiency
Differentiate your brand by demonstrating a commitment to quality and safety
Gain a competitive edge when working with retailers, suppliers, and certification bodies.
How Can Signify Help Transform Your Manufacturing Compliance?
In the highly regulated food manufacturing industry, ensuring compliance with evolving standards is both critical and challenging.
Signify offers an AI-driven compliance management platform that can help you transform how to navigate these complexities with ease.
Why Choose Signify?
Accelerate Time to Market: By automating compliance reviews, Signify reduces review times by up to 90%, enabling faster product launches without compromising safety or quality.
Proactive Risk Management: Signify's continuous monitoring system automatically detects changes in regulations and evaluates your documents in real-time, identifying potential compliance risks before they become issues.
Streamlined Supplier Verification: Ensure your suppliers meet necessary standards and regulations, enhancing confidence in your supply chain decisions.
Enhanced Audit Readiness: Maintain a comprehensive audit trail and traceability matrix, simplifying the process of demonstrating compliance to regulators and auditors.
Integrating Signify into your operations not only simplifies food manufacturing compliance but also positions your company as a leader in food safety and quality.
Embrace a smarter, more efficient approach to compliance management with Signify!
Book a demo today and discover how Signify can elevate your food manufacturing operations.
Food manufacturing compliance is about following the rules while also protecting public health, maintaining trust, and keeping operations running smoothly.
Regulatory requirements are strict for a reason, but instead of seeing them as hurdles, manufacturers should treat compliance as an opportunity to strengthen processes, improve efficiency, and ensure product quality.
The key is to understand the rules and make them a natural part of daily operations.
This guide breaks down the essentials, from regulatory frameworks to practical strategies that help you stay ahead of compliance challenges without disrupting production.
The Regulatory Framework for Food Manufacturing
Before diving into best practices, let’s go over the key regulatory agencies that oversee food manufacturing:
FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulates most food products and enforces the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) and Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP). These focus on proactive food safety measures.
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) oversees meat, poultry, and eggs. It enforces Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), which helps identify and control potential hazards.
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) ensures worker safety by enforcing sanitation and equipment safety regulations.
Understanding these requirements is only the first step because:
FSMA shifts food safety from a reactive model to a proactive one.
CGMP sets hygiene and sanitation standards.
HACCP establishes risk-based controls to minimize contamination.
Compliance is not a passive process. It requires a deliberate and systematic approach.

Now, let’s look at how to turn these regulations into effective practices.
4 Best Practices for Food Manufacturing Compliance
While regulations provide the framework, compliance requires a structured, ongoing commitment to food safety.
Here’s how manufacturers can ensure they meet and exceed regulatory requirements.
1. Develop a Strong Food Safety Plan
A food safety plan is not a suggestion. Most food businesses, including processors, retailers, and food service establishments, are legally obligated to have a food safety plan.
So, every facility must develop and maintain a structured plan that addresses potential risks and outlines clear preventive measures.
Core Components of an Effective Food Safety Plan
Hazard Identification: Assess biological, chemical, and physical hazards at every stage of production, including raw materials, storage, processing, and packaging.
Preventive Controls: Implement strict measures such as temperature control, cross-contamination prevention, and sanitation protocols.
Monitoring Systems: Use automated tracking tools like Signify and real-time data collection to ensure compliance with safety standards.

Corrective Actions: Establish predefined procedures for handling deviations, including product recalls and production shutdowns when necessary.
Employee Training: Require all personnel to undergo regular food safety education and demonstrate competency in hygiene, sanitation, and contamination prevention.

Rather than viewing compliance as a regulatory burden, as a manufacturer, you should integrate these processes into your standard operating procedures (SOPs) to enhance efficiency and food safety simultaneously.
2. Implement a Comprehensive Sanitation Program
Sanitation is more than a routine task. It is a critical control point that directly impacts food safety and regulatory compliance.
Poor sanitation can result in severe consequences, including product recalls, legal action, and reputational damage.
How to Build a Strong Sanitation Program
A Master Sanitation Schedule: Assign cleaning tasks to employees, outlining frequency and scope (e.g., daily equipment cleaning, weekly deep cleans). A structured schedule prevents the buildup of residue that can harbor bacteria.
Hygiene Protocols: Enforce handwashing, protective clothing use, and strict personal hygiene standards for employees. Implement "hygiene zones" within the facility where workers transition from regular areas to sanitized production spaces.
Sanitation Validation: Conduct ATP swab tests to verify cleanliness, ensuring sanitation processes are effective. ATP testing can help identify microbial contamination even when surfaces appear clean.
Allergen Management: Implement measures to prevent cross-contact between allergen-containing and allergen-free production lines. This may involve using dedicated equipment, labeling allergens clearly, and enforcing strict cleaning protocols between production runs.

3. Strengthen Supplier and Ingredient Traceability
Even the most carefully controlled manufacturing environment can be compromised by a weak supply chain.
Without full visibility into ingredient sourcing, manufacturers face significant risks, including contamination, fraud, and regulatory violations.
Key Strategies for Supply Chain Compliance
Supplier Audits: Regularly inspect supplier facilities and require compliance with industry certifications such as GFSI (Global Food Safety Initiative).
Ingredient Testing: Conduct microbiological and chemical testing of raw materials upon receipt.
Blockchain-Based Traceability: Use blockchain technology to create an unalterable record of ingredient origins, movement, and storage conditions.
Cold Chain Monitoring: Ensure temperature-sensitive products remain within safe limits during transport and storage.
Pro Tip:
Leverage Signify's Supplier Verification feature to confirm that all suppliers comply with relevant standards and regulations. This tool streamlines the verification process, enhancing confidence in selecting reliable and ethical suppliers.

4. Conduct Regular Compliance Audits and Emergency Preparedness Drills
Compliance isn’t a one-time effort. It requires continuous monitoring and improvement. So, invest time and effort into regular audits and emergency preparedness drills to stay ahead of potential risks.
Steps for an Effective Audit and Recall Plan
Routine Internal Audits: Conduct monthly inspections to ensure compliance with CGMP and HACCP requirements.
Third-Party Audits: Engage external auditors for unbiased evaluations and industry certification.
Mock Recalls: Test traceability systems by running simulated product recalls.
Staff Training on Crisis Management: Educate employees on proper response procedures for contamination incidents or regulatory inspections.
Pro Tip:
Achieve effortless compliance with AI checklists! Identify gaps, track progress, and maintain industry standards with dynamic, custom-tailored tools that boost efficiency.
This proactive approach eliminates the need for manual gap analysis and ensures that your operations are always aligned with current regulations.
Lessons in Food Safety
Here are examples of successful compliance programs in food manufacturing that demonstrate effective practices and strategies:
1. Mars, Inc.
Mars faced a significant challenge when it had to recall millions of confectionery bars due to contamination with plastic pieces.
The company utilized its efficient supply chain management systems and governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) controls to quickly identify the root cause of the issue.
They traced the contaminant back to a specific factory and tracked affected batches effectively, showcasing the importance of robust traceability systems in compliance management.
2. Blue Bell Creameries
After a listeria outbreak in 2015, Blue Bell Creameries overhauled its compliance program by implementing a comprehensive food safety plan that included stringent monitoring and preventive measures.
The company focused on improving sanitation practices, employee training, and hazard analysis, which helped restore consumer trust and ensure compliance with FDA regulations.
3. Chipotle Mexican Grill
Following multiple food safety incidents, Chipotle implemented a rigorous food safety audit program and enhanced staff training initiatives.
The company adopted a culture of compliance by involving employees at all levels in food safety practices and regularly conducting mock recalls to prepare for potential contamination events.
This way, they have significantly improved their compliance standing and operational efficiency.
4. Peanut Corporation of America
The 2009 Salmonella outbreak linked to Peanut Corporation of America highlighted the consequences of poor sanitation oversight.
In response, many companies in the industry adopted more stringent sanitation protocols and traceability measures to prevent similar incidents.
Compliance as Your Competitive Advantage
If you approach compliance as just another regulatory requirement, you are missing a powerful opportunity.
The most successful food manufacturers do not just aim to meet the bare minimum.
They build compliance into their company culture, making it a driver of efficiency, trust, and long-term growth.
When you take a proactive stance on food safety and compliance, you are not just protecting your business – you are strengthening it as well.
A well-structured compliance program reduces the risks of contamination, product recalls, and legal action. More importantly, it builds consumer confidence.
Shoppers are more informed than ever, and they expect transparency and accountability from the brands they trust.
By integrating food safety and sanitation into your everyday operations, you can:
Reduce costly disruptions by preventing regulatory violations before they happen
Streamline production with well-documented processes that improve efficiency
Differentiate your brand by demonstrating a commitment to quality and safety
Gain a competitive edge when working with retailers, suppliers, and certification bodies.
How Can Signify Help Transform Your Manufacturing Compliance?
In the highly regulated food manufacturing industry, ensuring compliance with evolving standards is both critical and challenging.
Signify offers an AI-driven compliance management platform that can help you transform how to navigate these complexities with ease.
Why Choose Signify?
Accelerate Time to Market: By automating compliance reviews, Signify reduces review times by up to 90%, enabling faster product launches without compromising safety or quality.
Proactive Risk Management: Signify's continuous monitoring system automatically detects changes in regulations and evaluates your documents in real-time, identifying potential compliance risks before they become issues.
Streamlined Supplier Verification: Ensure your suppliers meet necessary standards and regulations, enhancing confidence in your supply chain decisions.
Enhanced Audit Readiness: Maintain a comprehensive audit trail and traceability matrix, simplifying the process of demonstrating compliance to regulators and auditors.
Integrating Signify into your operations not only simplifies food manufacturing compliance but also positions your company as a leader in food safety and quality.
Embrace a smarter, more efficient approach to compliance management with Signify!
Book a demo today and discover how Signify can elevate your food manufacturing operations.
Food manufacturing compliance is about following the rules while also protecting public health, maintaining trust, and keeping operations running smoothly.
Regulatory requirements are strict for a reason, but instead of seeing them as hurdles, manufacturers should treat compliance as an opportunity to strengthen processes, improve efficiency, and ensure product quality.
The key is to understand the rules and make them a natural part of daily operations.
This guide breaks down the essentials, from regulatory frameworks to practical strategies that help you stay ahead of compliance challenges without disrupting production.
The Regulatory Framework for Food Manufacturing
Before diving into best practices, let’s go over the key regulatory agencies that oversee food manufacturing:
FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulates most food products and enforces the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) and Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP). These focus on proactive food safety measures.
USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) oversees meat, poultry, and eggs. It enforces Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), which helps identify and control potential hazards.
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) ensures worker safety by enforcing sanitation and equipment safety regulations.
Understanding these requirements is only the first step because:
FSMA shifts food safety from a reactive model to a proactive one.
CGMP sets hygiene and sanitation standards.
HACCP establishes risk-based controls to minimize contamination.
Compliance is not a passive process. It requires a deliberate and systematic approach.

Now, let’s look at how to turn these regulations into effective practices.
4 Best Practices for Food Manufacturing Compliance
While regulations provide the framework, compliance requires a structured, ongoing commitment to food safety.
Here’s how manufacturers can ensure they meet and exceed regulatory requirements.
1. Develop a Strong Food Safety Plan
A food safety plan is not a suggestion. Most food businesses, including processors, retailers, and food service establishments, are legally obligated to have a food safety plan.
So, every facility must develop and maintain a structured plan that addresses potential risks and outlines clear preventive measures.
Core Components of an Effective Food Safety Plan
Hazard Identification: Assess biological, chemical, and physical hazards at every stage of production, including raw materials, storage, processing, and packaging.
Preventive Controls: Implement strict measures such as temperature control, cross-contamination prevention, and sanitation protocols.
Monitoring Systems: Use automated tracking tools like Signify and real-time data collection to ensure compliance with safety standards.

Corrective Actions: Establish predefined procedures for handling deviations, including product recalls and production shutdowns when necessary.
Employee Training: Require all personnel to undergo regular food safety education and demonstrate competency in hygiene, sanitation, and contamination prevention.

Rather than viewing compliance as a regulatory burden, as a manufacturer, you should integrate these processes into your standard operating procedures (SOPs) to enhance efficiency and food safety simultaneously.
2. Implement a Comprehensive Sanitation Program
Sanitation is more than a routine task. It is a critical control point that directly impacts food safety and regulatory compliance.
Poor sanitation can result in severe consequences, including product recalls, legal action, and reputational damage.
How to Build a Strong Sanitation Program
A Master Sanitation Schedule: Assign cleaning tasks to employees, outlining frequency and scope (e.g., daily equipment cleaning, weekly deep cleans). A structured schedule prevents the buildup of residue that can harbor bacteria.
Hygiene Protocols: Enforce handwashing, protective clothing use, and strict personal hygiene standards for employees. Implement "hygiene zones" within the facility where workers transition from regular areas to sanitized production spaces.
Sanitation Validation: Conduct ATP swab tests to verify cleanliness, ensuring sanitation processes are effective. ATP testing can help identify microbial contamination even when surfaces appear clean.
Allergen Management: Implement measures to prevent cross-contact between allergen-containing and allergen-free production lines. This may involve using dedicated equipment, labeling allergens clearly, and enforcing strict cleaning protocols between production runs.

3. Strengthen Supplier and Ingredient Traceability
Even the most carefully controlled manufacturing environment can be compromised by a weak supply chain.
Without full visibility into ingredient sourcing, manufacturers face significant risks, including contamination, fraud, and regulatory violations.
Key Strategies for Supply Chain Compliance
Supplier Audits: Regularly inspect supplier facilities and require compliance with industry certifications such as GFSI (Global Food Safety Initiative).
Ingredient Testing: Conduct microbiological and chemical testing of raw materials upon receipt.
Blockchain-Based Traceability: Use blockchain technology to create an unalterable record of ingredient origins, movement, and storage conditions.
Cold Chain Monitoring: Ensure temperature-sensitive products remain within safe limits during transport and storage.
Pro Tip:
Leverage Signify's Supplier Verification feature to confirm that all suppliers comply with relevant standards and regulations. This tool streamlines the verification process, enhancing confidence in selecting reliable and ethical suppliers.

4. Conduct Regular Compliance Audits and Emergency Preparedness Drills
Compliance isn’t a one-time effort. It requires continuous monitoring and improvement. So, invest time and effort into regular audits and emergency preparedness drills to stay ahead of potential risks.
Steps for an Effective Audit and Recall Plan
Routine Internal Audits: Conduct monthly inspections to ensure compliance with CGMP and HACCP requirements.
Third-Party Audits: Engage external auditors for unbiased evaluations and industry certification.
Mock Recalls: Test traceability systems by running simulated product recalls.
Staff Training on Crisis Management: Educate employees on proper response procedures for contamination incidents or regulatory inspections.
Pro Tip:
Achieve effortless compliance with AI checklists! Identify gaps, track progress, and maintain industry standards with dynamic, custom-tailored tools that boost efficiency.
This proactive approach eliminates the need for manual gap analysis and ensures that your operations are always aligned with current regulations.
Lessons in Food Safety
Here are examples of successful compliance programs in food manufacturing that demonstrate effective practices and strategies:
1. Mars, Inc.
Mars faced a significant challenge when it had to recall millions of confectionery bars due to contamination with plastic pieces.
The company utilized its efficient supply chain management systems and governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) controls to quickly identify the root cause of the issue.
They traced the contaminant back to a specific factory and tracked affected batches effectively, showcasing the importance of robust traceability systems in compliance management.
2. Blue Bell Creameries
After a listeria outbreak in 2015, Blue Bell Creameries overhauled its compliance program by implementing a comprehensive food safety plan that included stringent monitoring and preventive measures.
The company focused on improving sanitation practices, employee training, and hazard analysis, which helped restore consumer trust and ensure compliance with FDA regulations.
3. Chipotle Mexican Grill
Following multiple food safety incidents, Chipotle implemented a rigorous food safety audit program and enhanced staff training initiatives.
The company adopted a culture of compliance by involving employees at all levels in food safety practices and regularly conducting mock recalls to prepare for potential contamination events.
This way, they have significantly improved their compliance standing and operational efficiency.
4. Peanut Corporation of America
The 2009 Salmonella outbreak linked to Peanut Corporation of America highlighted the consequences of poor sanitation oversight.
In response, many companies in the industry adopted more stringent sanitation protocols and traceability measures to prevent similar incidents.
Compliance as Your Competitive Advantage
If you approach compliance as just another regulatory requirement, you are missing a powerful opportunity.
The most successful food manufacturers do not just aim to meet the bare minimum.
They build compliance into their company culture, making it a driver of efficiency, trust, and long-term growth.
When you take a proactive stance on food safety and compliance, you are not just protecting your business – you are strengthening it as well.
A well-structured compliance program reduces the risks of contamination, product recalls, and legal action. More importantly, it builds consumer confidence.
Shoppers are more informed than ever, and they expect transparency and accountability from the brands they trust.
By integrating food safety and sanitation into your everyday operations, you can:
Reduce costly disruptions by preventing regulatory violations before they happen
Streamline production with well-documented processes that improve efficiency
Differentiate your brand by demonstrating a commitment to quality and safety
Gain a competitive edge when working with retailers, suppliers, and certification bodies.
How Can Signify Help Transform Your Manufacturing Compliance?
In the highly regulated food manufacturing industry, ensuring compliance with evolving standards is both critical and challenging.
Signify offers an AI-driven compliance management platform that can help you transform how to navigate these complexities with ease.
Why Choose Signify?
Accelerate Time to Market: By automating compliance reviews, Signify reduces review times by up to 90%, enabling faster product launches without compromising safety or quality.
Proactive Risk Management: Signify's continuous monitoring system automatically detects changes in regulations and evaluates your documents in real-time, identifying potential compliance risks before they become issues.
Streamlined Supplier Verification: Ensure your suppliers meet necessary standards and regulations, enhancing confidence in your supply chain decisions.
Enhanced Audit Readiness: Maintain a comprehensive audit trail and traceability matrix, simplifying the process of demonstrating compliance to regulators and auditors.
Integrating Signify into your operations not only simplifies food manufacturing compliance but also positions your company as a leader in food safety and quality.
Embrace a smarter, more efficient approach to compliance management with Signify!
Book a demo today and discover how Signify can elevate your food manufacturing operations.
The information presented is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be construed as legal, regulatory, or professional advice. Organizations should consult with qualified legal and compliance professionals for guidance specific to their circumstances.
4 Best Practices for Food Manufacturing Compliance
4 Best Practices for Food Manufacturing Compliance
Feb 28, 2025