Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Compliance - The Ultimate Guide
Mar 7, 2025
Pharmaceutical manufacturers in the United States face an intricate web of regulations that protect patient health.
Though requirements may seem demanding, clear strategies can help you navigate audits and maintain quality standards.
Let's go over 7 key pharmaceutical manufacturing compliance challenges and practical solutions you can adopt right now.
Regulatory Landscape and Its Ongoing Evolution
Regulatory bodies, particularly the FDA, regularly update guidelines to address emerging technologies, data integrity concerns, and distribution complexities.
Moreover, the DSCSA continues to press for heightened tracking and serialization requirements, making supply chain transparency a priority for every manufacturer:
1. Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP):
Emphasize consistent quality from raw materials to the final product.
Careful documentation, rigorous validation, and frequent training are required to ensure uniform processes are followed.
2. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA):
Mandates interoperable systems for tracking prescription drugs at every stage.
Introduces serialization rules that ensure each product can be followed from manufacturing to dispensing.
3. Ongoing FDA Guidance Updates:
Highlight the importance of data security and real-time monitoring.
Encourage continuous improvement in manufacturing methods, especially as companies adopt new technologies.
Pro Tip:
A dedicated team or point person who tracks FDA announcements and DSCSA deadlines can help you quickly translate evolving requirements into updated Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and training sessions.
However, instead of spending weeks manually reviewing policies and procedures, Signify automates compliance assessments, instantly identifying gaps and ensuring audit-ready traceability.
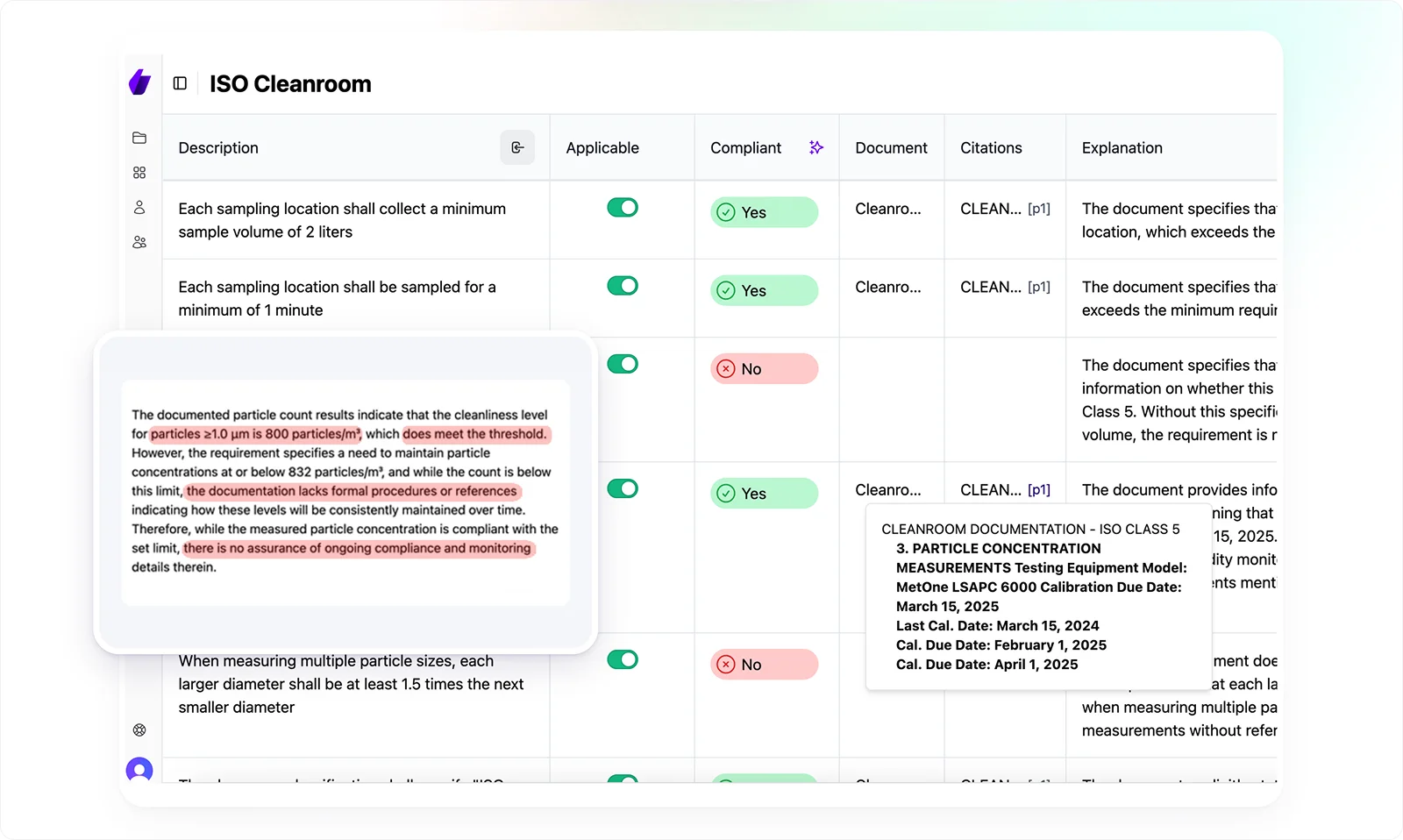
With AI-powered analysis and smart checklists, your team can prioritize critical compliance risks and focus on strategic remediation rather than sifting through documents.
7 Key Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Compliance Challenges
Below are seven recurring challenges and solutions to maintain compliance in a way that protects both quality and business continuity.
Challenge 1: Outdated or Ambiguous Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are the foundation of consistent and controlled pharmaceutical production. If they are outdated, unclear, or incomplete, employees may rely on personal judgment, leading to inconsistent outcomes.
Regulators often review SOPs first during audits to assess whether processes are well-defined. When SOPs don’t align with real-world practices, it signals weak internal controls and increases the risk of compliance issues.
Solutions
1. Create Frequent SOP Reviews with Cross-Functional Input
What to Do: Establish a review cycle (every six or twelve months) to reevaluate SOPs.
During these reviews, invite representatives from production, quality, maintenance, and even IT (if processes involve software or automation).
Why This Works: Getting diverse perspectives ensures SOPs align with actual operations. For instance, an operator may point out shortcuts taken on the floor, while a QC analyst might highlight unaddressed testing parameters.
2. Use Clear Structure and Terminology
What to Do: Adopt a standardized format that outlines each procedure step-by-step, uses consistent headings (e.g., purpose, scope, responsibilities, procedure, references), and defines key terms at the outset.
Why This Works: A uniform structure helps staff quickly locate relevant sections and reduces misinterpretation. Clear language also prevents confusion about tasks such as sampling or batch record completion.
3. Employ a Digital Repository for Version Control
What to Do: Move SOP storage from binders or shared drives to a secure document management system. You can also require an approval workflow so any changes undergo review and sign-off by authorized personnel.
Why This Works: Version control guarantees everyone accesses the latest approved SOP. Audit trails within the system show who made changes, when, and why, which is useful for demonstrating procedural updates to the FDA.
Challenge 2: Data Integrity Pitfalls
Data integrity has become a top enforcement priority for the FDA.
Missing records, manual alterations, or inadequate audit trails can undermine confidence in product quality.
Still, facilities relying heavily on paper-based logs are especially vulnerable to human error, while improperly configured electronic systems may leave gaps regulators can exploit.
For example, even small discrepancies (like an unexplained timestamp) can raise doubts about an entire batch’s legitimacy.
Solutions
1. Transition from Paper to Electronic Batch Records (EBRs)
What to Do: Implement an EBR system that captures production data in real-time. Ensure it includes automated time stamps, user logins, and workflow checks to minimize manual data entry.
Why This Works: Digital records reduce transcription errors and support robust audit trails, making it harder to modify or falsify data without detection.
2. Implement Stringent Access Controls
What to Do: Assign role-based permissions so that only authorized users can edit or approve records. Require multifactor authentication (MFA) for critical systems.
Why This Works: Limiting system access prevents unauthorized changes. Clear user roles help track accountability, discouraging employees from tampering with data.
3. Conduct Regular Data Audits and Anomaly Detection
What to Do: Conduct quarterly or monthly reviews of electronic logs, checking for suspicious patterns such as frequent after-hours edits. Use software that flags irregularities or changes made outside normal processes.
Why This Works: Proactive monitoring helps catch potential data manipulation early. It also reassures inspectors that the company routinely validates data accuracy.
Challenge 3: Laboratory Control Gaps
Laboratories verify that each drug batch meets safety and efficacy standards before release. Poorly validated methods or missing documentation can lead to serious consequences like delaying compliant batches due to inconsistencies or allowing subpar products to reach the market.
Because of their direct impact on product quality, regulators closely examine laboratory processes, making any gaps in validation or record-keeping a compliance risk.
Solutions
1. Use Method Validation and Ongoing Verification
What to Do: Thoroughly validate each analytical test method under conditions replicating actual usage. Periodically verify performance (e.g., through system suitability tests) to maintain reliability.
Why This Works: Consistent, repeatable methods help confirm a product’s attributes (e.g., potency, purity). Regular re-validation ensures methods remain effective despite minor shifts in reagents or equipment.
2. Automate Lab Processes
What to Do: Use instruments connected to a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) that captures data automatically. Integrate devices like chromatographs or spectrophotometers for direct data transfer.
Why This Works: Automation reduces transcription errors. Direct data capture also speeds up analysis, enabling real-time comparisons of current runs vs. historical baselines.
3. Do Intensive Lab Staff Training
What to Do: Offer specialized modules on advanced instruments, data interpretation, and documentation practices. Encourage a culture of questioning any suspicious result rather than discarding it.
Why This Works: Skilled, vigilant technicians are more likely to spot anomalies or potential contamination. Proper training also reinforces the importance of compliance in day-to-day tasks.
Challenge 4: Equipment Maintenance & Calibration Gaps
Manufacturers rely on complex equipment (reactors, fillers, packaging lines) that must be kept within strict operating parameters.
Delays or lapses in maintenance can introduce variability, leading to inconsistent batch quality or, in worse cases, complete production stoppages.
Regulators also examine maintenance logs for evidence of systematic upkeep, and any discrepancies may raise doubts about overall process control.
Solutions
1. Perform Preventive Maintenance (PM) Scheduling
What to Do: Plan maintenance intervals based on manufacturer recommendations, historical data, and operational intensity. Tie these intervals to computerized systems that generate alerts for upcoming tasks.
Why This Works: Regular PM addresses issues before they become major breakdowns, ensuring minimal unplanned downtime and consistent process performance.
2. Use Predictive Analytics and Condition Monitoring
What to Do: Install sensors (temperature, vibration, pressure) on critical machinery and feed these readings into an analytics platform that identifies abnormal trends.
Why This Works: Early detection of deviations helps maintenance teams fix issues preemptively so potential failures don’t disrupt production. This approach can also extend equipment life and improve resource allocation.
3. Calibrate Traceability
What to Do: Maintain a calibration log that documents the date, technician, and test standards for each calibration. Keep calibration certificates and associated data in a central, easily searchable database.
Why This Works: Clear documentation demonstrates consistent calibration practices to inspectors. It also helps you quickly identify the root cause if a product deviation is traced back to equipment accuracy.
Challenge 5: Communication Silos and Disconnected Teams
Pharmaceutical production involves multiple disciplines like production staff, quality control, regulatory affairs, supply chain management, and more.
When these groups operate in silos, essential details can fall through the cracks.
Consequently, a minor deviation in one department might snowball into a major compliance lapse if unresolved due to poor communication.
Solutions
1. Organize Cross-Departmental Meetings and Dashboards
What to Do: Hold regular (e.g., weekly) sync meetings where representatives from each department share updates, upcoming changes, and potential risks. Use a centralized dashboard for metrics like deviation rates, equipment uptime, and on-time batch releases.
Why This Works: Transparency in performance metrics and open communication minimize surprises. Everyone knows where bottlenecks are and can collaborate on solutions.
2. Align Departmental KPIs
What to Do: Set overlapping performance indicators – for instance, make “percentage of compliant batches released on time” a metric shared by both production and QA.
Why This Works: When teams share accountability for the same outcome, they are more likely to cooperate, recognizing how each department’s performance affects the other’s success.
3. Structure Handoffs and Escalation Paths
What to Do: Create a formal escalation procedure for unresolved deviations, equipment issues, or documentation discrepancies. Clarify which manager or department must be notified at each step.
Why This Works: A predefined chain of command reduces finger-pointing. Problems are elevated quickly to individuals with the authority and resources to solve them, preventing small concerns from growing into bigger violations.
Challenge 6: Evolving Regulatory Expectations
The FDA routinely revises guidance documents to address new technologies and methodologies.
Simultaneously, acts like the Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) impose serialization and tracing requirements that grow stricter over time.
As a manufacturer, if you ignore these shifts may find yourself suddenly out of compliance, requiring costly last-minute fixes.
Solutions
1. Early Engage with Regulators
What to Do: If planning a novel manufacturing approach or a significant process change, request a pre-submission meeting with the FDA. Present your proposed strategy and validation data.
Why This Works: Early feedback helps you align with regulatory expectations, reducing the risk of rework if the agency raises concerns post-implementation.
2. Try Scalable Systems and Processes
What to Do: Design your SOPs, data systems, and training programs to accommodate new guidelines without major overhauls. This might involve modular software or adjustable workflows.
Why This Works: When regulations change, you only need to revise specific segments rather than redesign everything from scratch. This agility lowers transition costs and accelerates compliance updates.
Challenge 7: Integrating Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Technologies such as continuous manufacturing, process analytical technology (PAT), and machine learning (ML) promise improved efficiency and real-time quality assurance.
Yet adopting them demands thorough validation, staff training, and updated SOPs
. Failing to integrate these tools correctly can undermine their benefits and invite regulatory concerns about data quality or process control.
Solutions
1. Phase Implementation and Pilot Programs
What to Do: Roll out advanced technologies on a limited scale – perhaps on a single product line – to gather performance metrics and refine the setup. Use real-time data to compare the pilot line’s output with that of conventional processes.
Why This Works: Starting small allows you to fix issues before full-scale adoption. You also collect credible data to demonstrate efficacy and compliance to inspectors.
2. Use Comprehensive Validation Protocols
What to Do: Develop clear validation plans for new equipment or software, covering installation qualification (IQ), operational qualification (OQ), and performance qualification (PQ). Document every test thoroughly.
Why This Works: Regulators expect proof that new technologies consistently meet quality standards. Detailed validation records confirm you’ve assessed risks and mitigated them effectively.
3. Focus on Employee Upskilling and Collaboration
What to Do: Provide focused training for operators, engineers, and QC analysts on how the new technology works, how data is interpreted, and which SOPs have changed. Encourage frequent feedback from these teams on usability and workflow impact.
Why This Works: Staff who understand the rationale and mechanics behind advanced systems are less likely to bypass or misuse them. Their buy-in also helps refine processes so that technology aligns with day-to-day realities.
Stay Ahead of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Compliance Challenges with Signify
Navigating regulatory compliance is complex, but Signify simplifies the process, reducing manual effort and ensuring accuracy across documentation, risk assessments, and regulatory tracking.
With AI-powered automation, Signify helps you:
Monitor regulatory updates in real-time – Stay ahead of evolving requirements without manual tracking.
Automate regulatory document reviews – Identify compliance gaps in policies, SOPs, and records instantly.
Ensure audit readiness – Maintain structured workflows and full traceability of compliance records.
Reduce compliance risks – AI-driven assessments detect misalignments before they lead to non-conformities.
Streamline remediation efforts – Get clear, actionable steps to correct compliance issues efficiently.
Don’t let compliance challenges slow you down.
Book a demo today and see how Signify can help you stay ahead with confidence.
